Core Banking Systems (CBS) refers to a standard IT solution wherein a central shared database supports the whole banking application. The characteristics of CBS are:
- There is a standard database during a central server located at a knowledge Center, which provides a consolidated view of the bank’s operations..
- Branches function as delivery channels providing services to its customers.
- CBS is centralized Banking Application software that has several components which have been designed to meet the demands of the banking system.
- CBS is supported by advanced technology infrastructure and has high standards of business functionality.
- Core Banking Solution brings significant benefits such as a customer is a customer of the bank and not only of the branch.
- CBS is modular in structure and is capable of being implemented in stages as per requirements of the bank.
- A CBS software also enables integration of all third-party applications, including in-house banking software, to facilitate simple and complex business processes.
Core Banking Solution
Some examples of CBS software are given below. These are only illustrative and not exhaustive.
- Finacle: Core banking software suite developed by Infosys that provides universal banking functionality covering all modules for banks covering all banking services.
- FinnOne: Web-based global banking product designed to support banks and financial solution companies in dealing with assets, liabilities, core financial accounting and customer service.
- Flexcube: Comprehensive, integrated, interoperable, and modular solution that enables banks to manage evolving customer expectations.
- BaNCS: A customer-centric business model which offers simplified operations comprising loans, deposits, wealth management, digital channels and risk and compliance components.
- bankMate: A full-scale Banking solution which is a scalable, integrated ebanking systems that meets the deployment requirements in traditional and non-traditional banking environments. It enables communication through any touch point to provide full access to provide complete range of banking services with anytime, anywhere paradigm.
Further, there are many CBS software developed by vendors which are used by smaller and co-operative banks. Some of the banks have also developed in-house CBS software. However, the trend is for using high-end CBS developed by vendors depending on cost-benefit analysis and needs.
Core Banking Solution has become a mandatory requirement to provide a range of services demanded by customers and the competitive banking environment. This requires that most of bank’s branches access applications from centralized data centers. CBS for a bank functions not only as a heart (circulatory system) but also as a nervous system. All transactions flow through these core systems, which, at an absolute minimum, must remain running and responsive during business hours. These systems are usually running 24×7 to support Internet banking, global operations, and real time transactions via ATM, Internet, mobile banking, etc.
Key modules of CBS
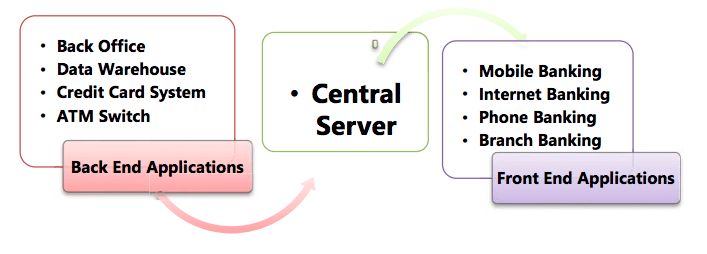
Back Office:
The Back Office is the portion of a company made up of administration and support personnel, who are not client-facing. Backoffice functions include settlements, clearances, record maintenance, regulatory compliance, accounting, and IT services. Back Office professionals may also work in areas like monitoring employees’ conversations and making sure they are not trading forbidden securities on their own accounts.
Data Warehouse:
Banking professionals use data warehouses to simplify and standardize the way they gather data – and eventually get to at least one clear version of the reality . Data warehouses lookout of the difficult data management – digesting large quantities of knowledge and ensuring accuracy – and make it easier for professionals to research data.
Credit-Card System:
Credit card system provides customer management, credit card management, account management, customer information management and general ledger functions; provides the online transaction authorization and service of the bank card in each transaction channel of the issuing bank; Support in the payment application; and at the same time, the system has a flexible parameter system, complex organization support mechanism and product factory based design concept to speed up product time to market.
Automated Teller Machines (ATM):
An Automated Teller Machine (ATM) is an electronic banking outlet that permits customers to finish basic transactions without the help of a branch representative or teller. Anyone with a mastercard or open-end credit can access most ATMs. ATMs are convenient, allowing consumers to perform quick, self-serve transactions from everyday banking like deposits and withdrawals to more complex transactions like bill payments and transfers.
Central Server:
Initially, it used to take at least a day for a transaction to get reflected in the real account because each branch had their local servers, and the data from the server in each branch was sent during a batch to the servers within the data center only at the top of the day (EOD). However, nowadays, most banks use core banking applications to support their operations creating a Centralized Online Real-time Exchange (or Environment) (CORE). This means that all the bank’s branches access applications from centralized data centers/servers, therefore, any deposits made in any branch are reflected immediately and customer can withdraw money from any other branch throughout the world.
Internet Banking
also referred to as Online Banking, is an electronic payment system that permits customers of a bank or other financial organization to conduct a variety of monetary transactions through the financial institution’s website. The online banking system offers over 250+ services and facilities that give us real-time access to our bank account. We can make and receive payments to our bank accounts, open Fixed and Recurring Deposits, view account details, request a cheque book and a lot more, while you are online.
Mobile Banking
Mobile Banking is a service provided by a bank or other financial that allows its customers to conduct financial institution that allows its customers to conduct financial transactions remotely using a mobile device like a Smartphone or tablet. Unlike the related internet banking, it uses software, usually called an app, provided by the financial organization for the aim . Mobile banking is typically available on a 24-hour basis
Phone Banking:
It is a functionality through which customers can execute many of the banking transactional services through Contact Centre of a bank over phone, without the need to visit a bank branch or ATM. Registration of Mobile number in account is one of the basic perquisite to avail Phone Banking. The use of telephone banking services, however, has been declining in favor of internet banking. Account related information, Cheque Book issue request, stop payment of cheque, Opening of Fixed deposit etc. are some of the services that can be availed under Phone Banking.
Branch Banking:
CBS are the bank’s centralized systems that are responsible for ensuring seamless workflow by automating the frontend and backend processes within a bank. CBS enables single-view of customer data across all branches in a bank and thus facilitate information across the delivery channels. The branch confines itself to the following key functions:
- Creating manual documents capturing data required for input into software;
- Internal authorization;
- Initiating Beginning-Of-Day (BOD) operations;
- End-Of-Day (EOD) operations; and
- Reviewing reports for control and error correction.
To conclude, CBS implementation has cut down time, working at the same time on dissimilar issues and escalating usefulness. The platform where communication technology and information technology are merged to suit core needs of banking is known as core banking solutions.
Here, computer software is used to perform core operations of banking like recording of transactions, passbook maintenance, and interest calculations on loans & deposits, customer records, balance of payments and withdrawal. Normal core banking functions will include deposit accounts, loans, mortgages and payments. Banks make these services available across multiple channels like ATMs, Internet banking, and branches.
Recommended Articles
